Chatbot Script Examples and Writing Tips for Customer Service
A practical guide with handy chatbot script examples. Feel free to copy and paste!
Written by Tetiana Shataieva
If you typed “How to write chatbot scripts” in your search box, you must have recognized the value and benefits a bot is going to bring to your business. Indeed, bots are huge resource savers for a company and great experience boosters for its customers.
In fact, 62% of customers prefer using a bot rather than waiting for an agent to respond (how about that human touch, huh?). It will streamline your service flows by bringing automation into them and raise the level of customer satisfaction a notch or two.
That is, of course, if you set up everything right. If you are here, it means that you have done your research, found the right tool from the myriad of chatbot platforms, and are now sitting with a pen poised over a blank sheet thinking “What in the world will my chatbot say?”
In this case, you are in the right place. I am going to walk you through the whole process of writing a chatbot script for your customer service, and even throw in some sample scripts that you are welcome to use.
How do chatbots work?
At the most general level, customer service chatbots fall into two main categories: rule-based and AI. Let’s look at them briefly to see how they work.
1. Rule-based bots, as the name suggests, operate on a set of rules that you program for them. Their responses to users are triggered either by the choice the user makes or the keyword they recognize. There is a dialogue “tree” behind such conversations, where for each response a certain scenario is prescribed. Simple as that.
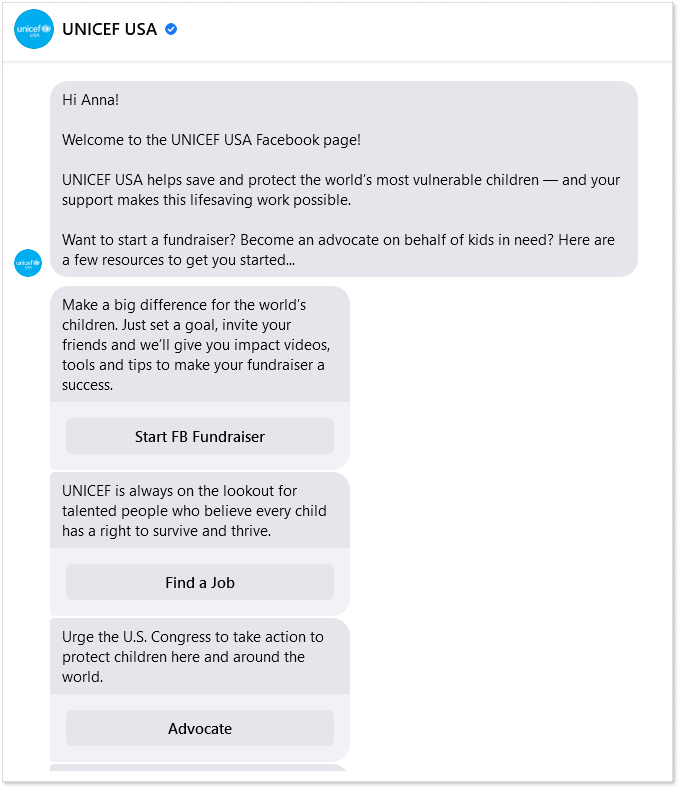
For example, UNICEF uses the rule-based approach in its Facebook Messenger. Depending on the user’s choice, the bot supplies the corresponding information.
2. AI chatbots have artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NPL) in their core and, as a result, can hold much more flexible conversations on various topics.
The bot learns from each dialogue it holds and improves itself in the process. The most sophisticated AI bots can mimic human conversation rather well. One of the best-known examples is the famously creepy Replika, a bot that sometimes sounds too much like a real person.
For the purposes of customer service and support, a rule-based chatbot is more than enough. In general, you can benefit from this machine in many ways depending on its type, but some of the best practices for chatbots are usually related to customer service. OK, let’s talk about bot scripts 😉
What is a chatbot script?
There are many situations in life when you need a script – when you are planning a lecture, presentation, or speech when you are getting ready for important negotiations, or an artistic performance, or any other compelling content. Customer service scenarios need scripts, too, as scripts allow them to cover most of the possible cases and also remember the human touch.
To get a relevant answer by all means, support agents use scripts, too. For example, implementing a chat script makes agents’ lives much easier and creates highly professional impressions.
Chatbot scripts, however, are never a “nice-to-have”, they are rather a “must-have”. Without a script, your virtual assistant will be silent. It can “say” only the things that you program it to say. This is, basically, what a script is – a set of pre-programmed responses and actions that a bot should execute under certain conditions.
For example, when a user opens the chat, the chatbot issues a welcome message. When the user’s message contains the word “delivery”, the bot offers a link to the delivery conditions. Easy as one-two-three, isn’t it?
Yes and no. It seems so simple at a glance, but in fact, a truly successful chatbot script is a product of hard work and thorough testing. You must not miss a single conversation turn and use all strategic points to create the best user experience.
How to write a chatbot script?
Now comes what you have been waiting for – a practical step-by-step guide for writing chatbot scripts with useful tips and examples.
Tools you can use in chatbot script creation
At this point, you must have already chosen a customer communication platform where you will run your bot. Otherwise, it’s high time to do so. For example, if your website is hosted on WordPress, you can select the best chatbot for WordPress based on this review.
Often, a platform that you have opted for includes a website chatbot builder where you can create all sorts of conversations for all possible scenarios. However, you can use any drawing software, such as Diagrams.net, Lucidchart, or Google Drawings, to sketch sequences and plan responses. Open an empty canvas and knock yourself out.
For example, this simple sequence took about five minutes to create in Google Drawings.
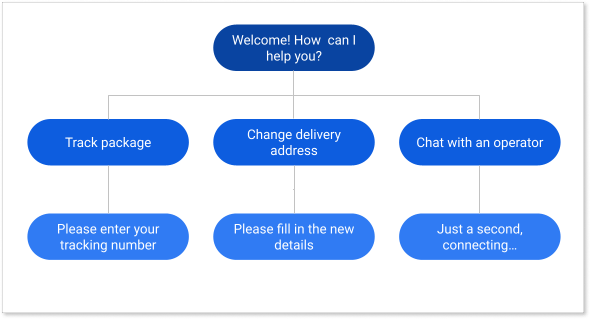
Guide to writing a chatbot script
OK, now roll up your sleeves, and let’s write some scripts. Follow the steps below to give voice to your customer service bot.
Map your user journey
Before you start writing, think about where you would like your customers to interact with the chatbot. The best idea is to look at the buyer’s journey and see where they might need a little help. This is where a bot should pop up. By the way, mapping a user journey is always recommended, whether you are using live chat or chatbot as your customer support channel.
Depending on the journey stage, the script will be different. A bot on the homepage and a bot on the checkout page will need different phrases to address the visitor. The one on the homepage may be more focused on lead generation and open up with an offer to subscribe or book a demo.
A checkout page bot will be more on the support side and ask if the customer needs assistance. By the way, when you map out the journey, do not forget about creating and processing your buyer persona – these two together create a powerful synergy and provide more insights.
Define the goal of your chatbot
Continuing the topic of the previous paragraph, let’s think of what you want your chatbot to do. Is it meant to offer support, direct customers to the product pages, collect their details, or make updates on their behalf?
Answers to these simple questions will help you shape the chatbot script scenario and decide whether you will need any calls-to-action and where you might place them. See the sample flow below, designed to offer a special discount to the customer. The messages and the corresponding CTAs serve this purpose.
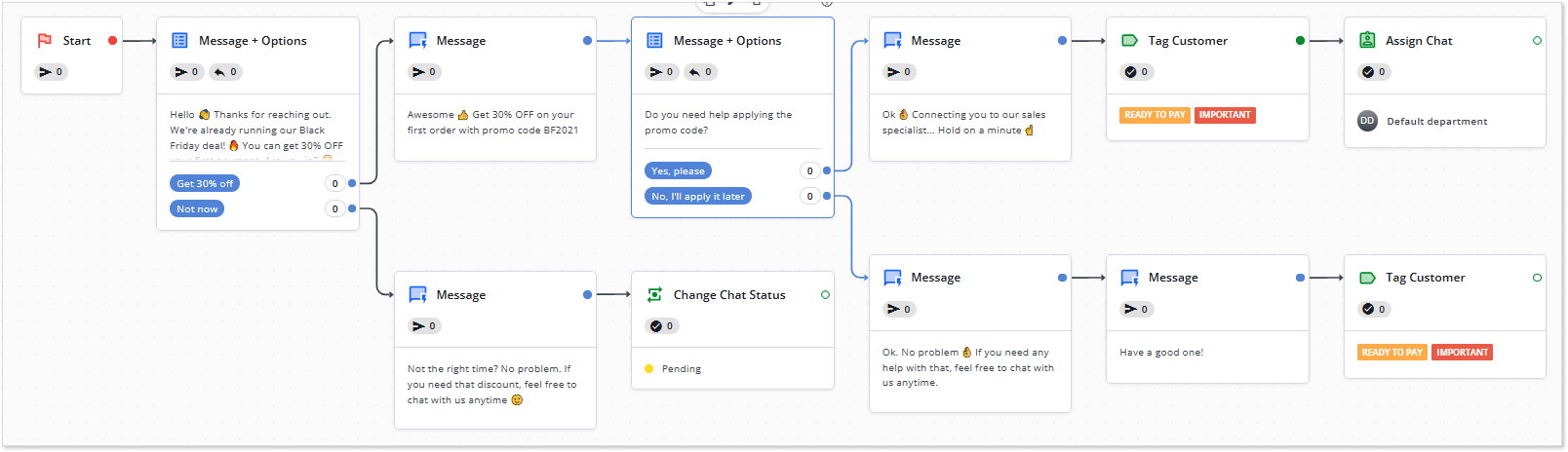
This conversation flow is created with the chatbot builder powered by HelpCrunch, where you can compile chatbot scripts from scratch, use one of the available templates, and edit them to fit your purposes.
Design its personality
You will never fool customers into believing they are chatting with a real person. Moreover, 48% of customers do not care about the chatbot’s personality as long as it can help them resolve their issues.
Nevertheless, your bot should have a personality, as it contributes to building an emotional bond with the customer. Besides, it is a part of your brand image, adding to its recognition. Even though it is just a piece of software, give it a face, a name, and a voice tone according to your customer service standards. Make it one of the action points of your chatbot UI design.
Think of the general tone. Light and humorous or no-nonsense and professional? Of course, that depends on the nature of your business. If you are a bank, a cool, professional approach will be more appropriate. If you are a vacation planning agency, you can go with an easy and friendly tone of voice to set the mood.
By the way, should your bot be male or female? Again, it depends. The most surefire way is to make your bot gender-neutral. This way, you will make users focus only on the real conversation and not distract them by the bot’s gender.
Build a dialogue tree
Anticipate all possible scenarios that customer conversations might have and build a dialogue for each of them. Think of the most common inquiries customers make and proceed from them. Make sure you have responses for all the most frequent requests, such as issue reports, price inquiries, questions about deliveries and refunds, and billing and invoice issues. A good idea may be to prepare different responses for the same questions and rotate them. This way, you will make your robot sound more “human”.
The example below shows a chatbot flow intended to collect information about issues upfront. By the way, you can find this script template on the HelpCrunch platform, too. This chatbot script template includes four possible conversation scenarios depending on the customer’s choice. A dialogue tree in its pure form.
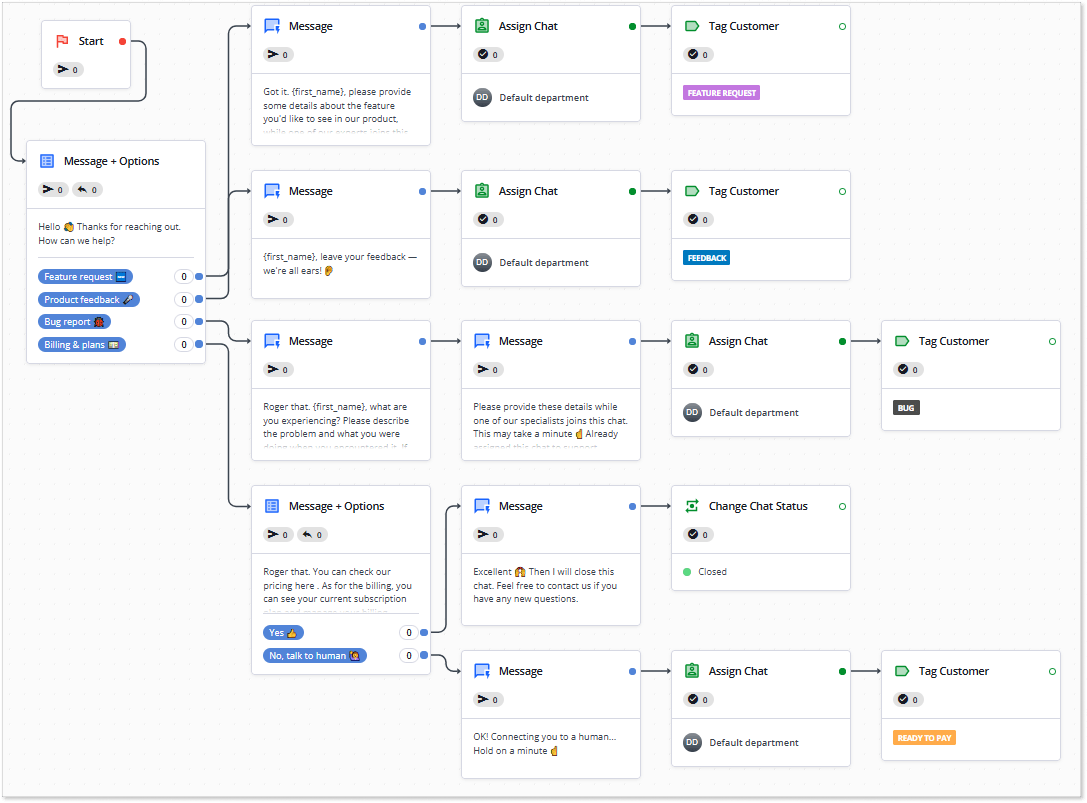
Write all chatbot messages
Now, it’s time to actually compile your chatbot scripts. Write all the conversational messages and calls-to-action you are planning to use in each script. These will be the actual responses your customers will see while communicating with your bot. Here are a couple of tips to help you write messages for your chatbot script:
- Design welcome messages and conversation finishers. While creating your bot personality, you should have found the right tone of voice that it is to use. Follow the same tone in writing the messages with which the bot will greet customers and end conversations.
For example, for a neutral and professional tone, an appropriate welcome message may be: “Hello, welcome to Our Bank. How can I help you?” If you have opted for a more informal and humorous tone, you may write your welcome message as follows: “Hey, how are you today? Planning your well-deserved vacation?”
- Personalize the conversation. If you use an account-based approach, you will know the name of the customer. Use it in chatbot communication. It will give a nice personal touch that customers like.
Also, calling the customer by name has a very practical value, too. When a bot says “Hello, Anna, what can I do for you today?”, I don’t go all starry-eyed because it called me by my name. I realize that in the background, it has pulled up my file from the CRM system and has all the info it may need to resolve my case. So, use names.
- Match the user’s sentiment. You have already built the chatbot dialogues, haven’t you? Well, then you should know which mood the user may have in each of them.
When they reach out to resolve a bug, they are, most probably, frustrated and a bit angry. When they want to inquire about a product or a special offer, they are relaxed and in a buying mood.
Match your messages to the customer’s sentiment every time.
For example, it won’t be a good idea to respond to a bug report with something like “Oops, it is surely not your lucky day.” Rather, give a neutral but emphatic response: “I am sorry that you have experienced an issue with our product. May I ask for more details to find a way to resolve it?”
- Use GIFs, emojis, and small talk, where appropriate. You are making a bot sound like a real human agent, because we humans often include GIFs and emojis in our messages instead of words. However, responses overloaded with emojis often annoy us even in conversations with real people, so use them in moderation, and only when they fit the general tone and user sentiment.
- Proofread the text. When you are finished drafting your text, check it for typos and grammar errors. Then show it to someone else who has not been involved in creating these chatbot scripts. Anyone looking at them with a fresh set of eyes should have no difficulty understanding what you mean to say.
Also, make sure your messages are not too long. Any sentence longer than three or four lines may make the customer lose engagement. Don’t quote whole chapters of your knowledge base, offer a link instead.
Place links strategically
Speaking of links – think about where you can supplement your bot messages with links and attachments, for example:
- Links to knowledge base articles upon certain keywords used by the customer
- Links to the product catalog at the opening of the conversation
- Links to the delivery and refund terms when the customer makes a corresponding inquiry
Think where the chatbot may hand the dialogue over to an agent
There will be cases that the robot cannot resolve. This is where an agent should take over the chat and handle the inquiry. Plan for such situations and write the corresponding messages. For example, you can offer an option to connect to an agent and, if the customer accepts it, the bot should transfer the chat.
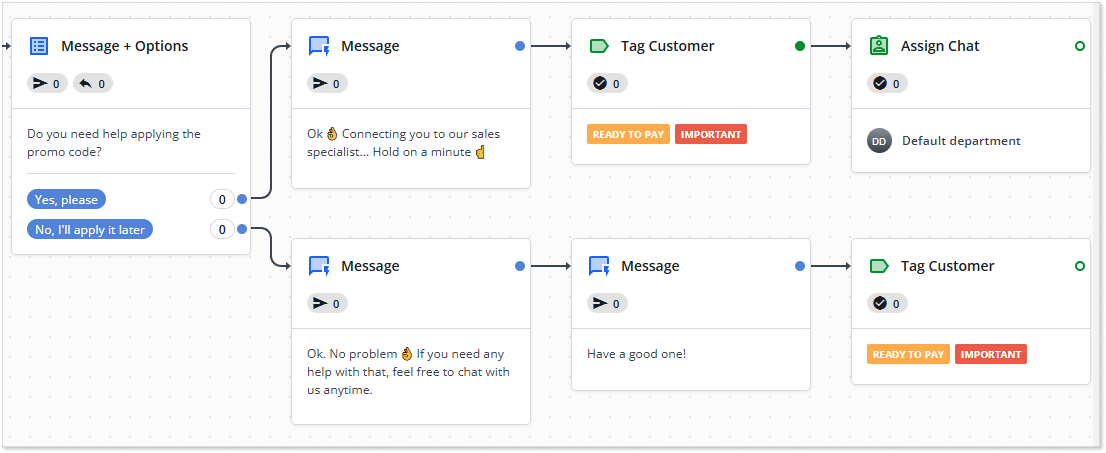
Do A/B testing
Run different versions of your chatbot scripts as part of overall A/B testing. Do not shrug off this activity on mobile devices, too. The metrics you collect will highlight successful solutions and areas of improvement.
See, for example, how different welcome messages perform in engaging visitors in a chat. Another metric worth monitoring is the self-service rate, showing how often the bot can resolve issues independently, without human intervention.
Include a rating in a chatbot widget, inviting customers to evaluate their conversational experience of communicating with the chatbot. Such ratings may also be a useful source of information about the bot’s performance.
Finally, you will be able to put together a chatbot script that works best for you.
Be ready to update and improve your scripts as needed
As you collect chatbot analytics, you will see which options are selected the most often and which are ignored, which user questions it can and cannot recognize, and where the conversation was or wasn’t successful. Armed with this data, you can update your chatbot script to make it more effective and usable.
For example, if you see a variant of the same question that often occurs, but the bot cannot provide quick replies, include a response to this question in your script. If your script says: “Would you like to benefit from our special conditions?” and customers keep choosing “Maybe, later”, it can be a sign for you to choose an easier tone and rephrase as follows: “Check out our special offer”.
Chatbot script examples and templates for customer service
Now, as promised, we have gathered some chatbot script examples that you can use in your customer service. All of them have that ultimate human touch. Feel free to just copy and paste any chatbot script sample to your bot scenario!
Chatbot welcome message:
- Hello, [username], welcome to [our company]! How can I help you?
- Hi, [username], how are you doing? What can I do for you today?
Report an issue:
- I am sorry that you have issues with our product. Please give me more details about what is wrong.
- That’s not good. Please describe what is wrong, and I will try to help you.
Update account:
- Of course, [username], please enter your new details in the form.
- Sure thing, type your further details, and I will update your profile for you.
Request information:
- Please tell me what you would like to learn about. I will be glad to assist you!
- Sure, happy to help. I know a lot about [our product], just tell me what you want to learn about.
Talk to an agent:
- Please wait while I am connecting you with our customer success manager.
- Just a sec, I am connecting you.
Agents are offline:
- Our agents will be back at [time]. Please leave a message, and we will get back to you ASAP.
- Oops! It looks like no one is at the office now. Just leave us a message, and we will text you back within the next 24 hours.
Links to the knowledge base or FAQ:
- Please see this article on [subject].
- Check out this article, it might have what you need.
Pause in the dialogue:
- Is there anything else I can help you with?
- Anything else I can do for you today?
Request not recognized:
- Sorry, I don’t think I understand. May I connect you to an agent?
- Oops, didn’t get that. Would you please rephrase your request?
Ending a conversation:
- Thanks for chatting, have a nice day!
- It was great talking to you, see you soon!
Of course, these chatbot scripts are far from exhaustive, but they just might spark your creativity. Add them to your bot design, mix, amend, and tweak as necessary.
Ready to launch your chatbot?
You are now all set to start using your very own bot. It has its unique personality reflecting your branding, it runs on a reliable platform, and now you have given it a voice of its own. Launch it, and see how it boosts customer experience and improves the performance of your customer support team.