We’re thrilled to unveil a new feature of our platform — Role-Based-Account-Access (RBAC)! Now, you can manage roles and grant access to different parts of our service with much more flexibility.
What’s RBAC?
RBAC, short for Role-Based-Account-Access, lets you configure roles and access rights flexibly, ensuring the right people have the right permissions. Companies benefit from RBAC by streamlining their workflow and enhancing security. It’s handy for organizations with diverse teams, allowing tailored access for different departments and roles, from administrators to support staff.
🔄 What’s changed?
Previously, you had just four default roles. With RBAC, you still have those defaults: Administrator, Supervisor, Agent, and now Support (formerly known as Agent chat-only). But now, in the Settings → Team section, you’ll find a new Roles & Permissions block. You can add custom roles and tweak access settings to your heart’s content there.
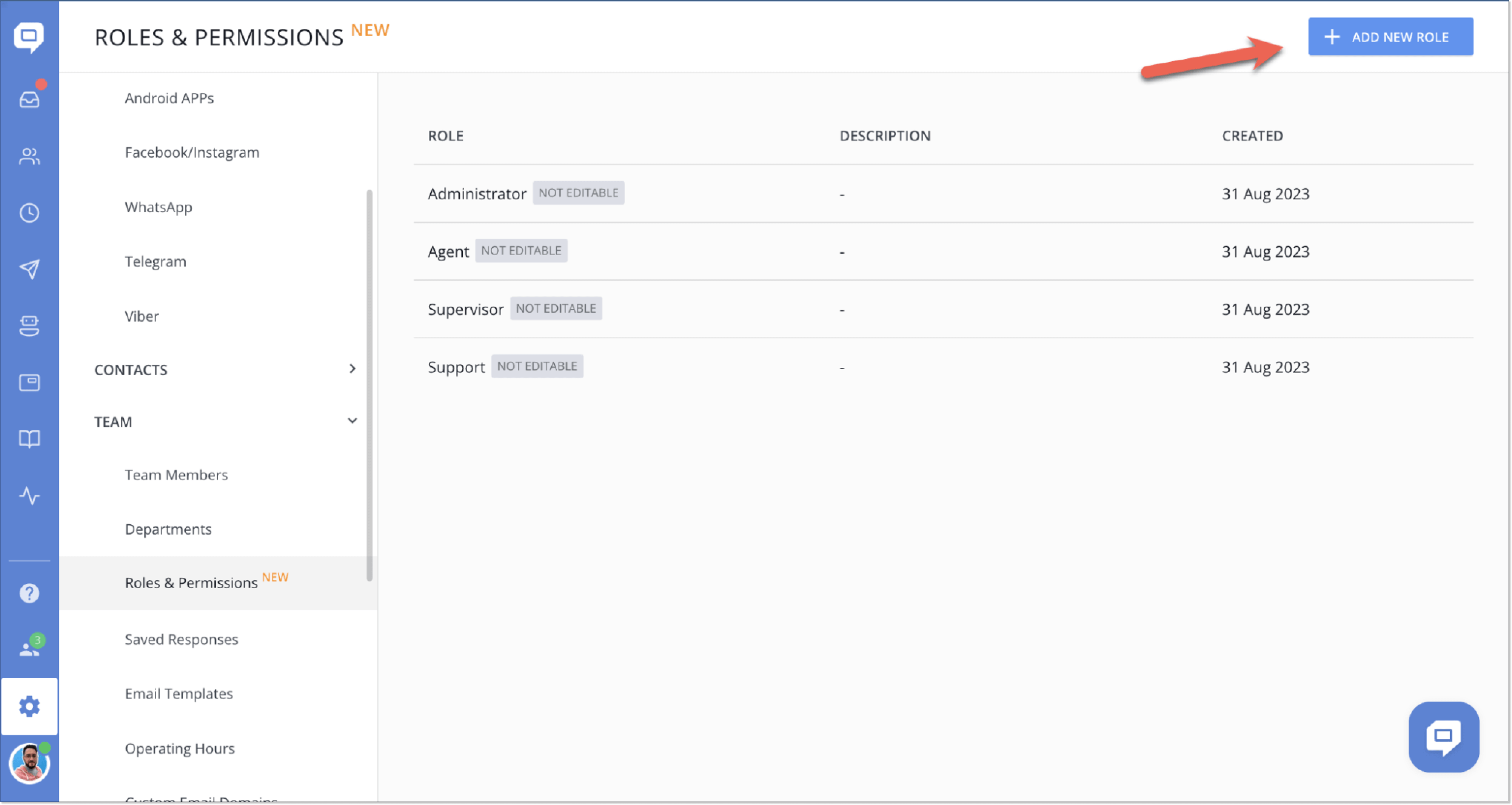
📝 How does it work?
When adding a custom role, you can fine-tune access to different service parts and even individual actions within those sections.
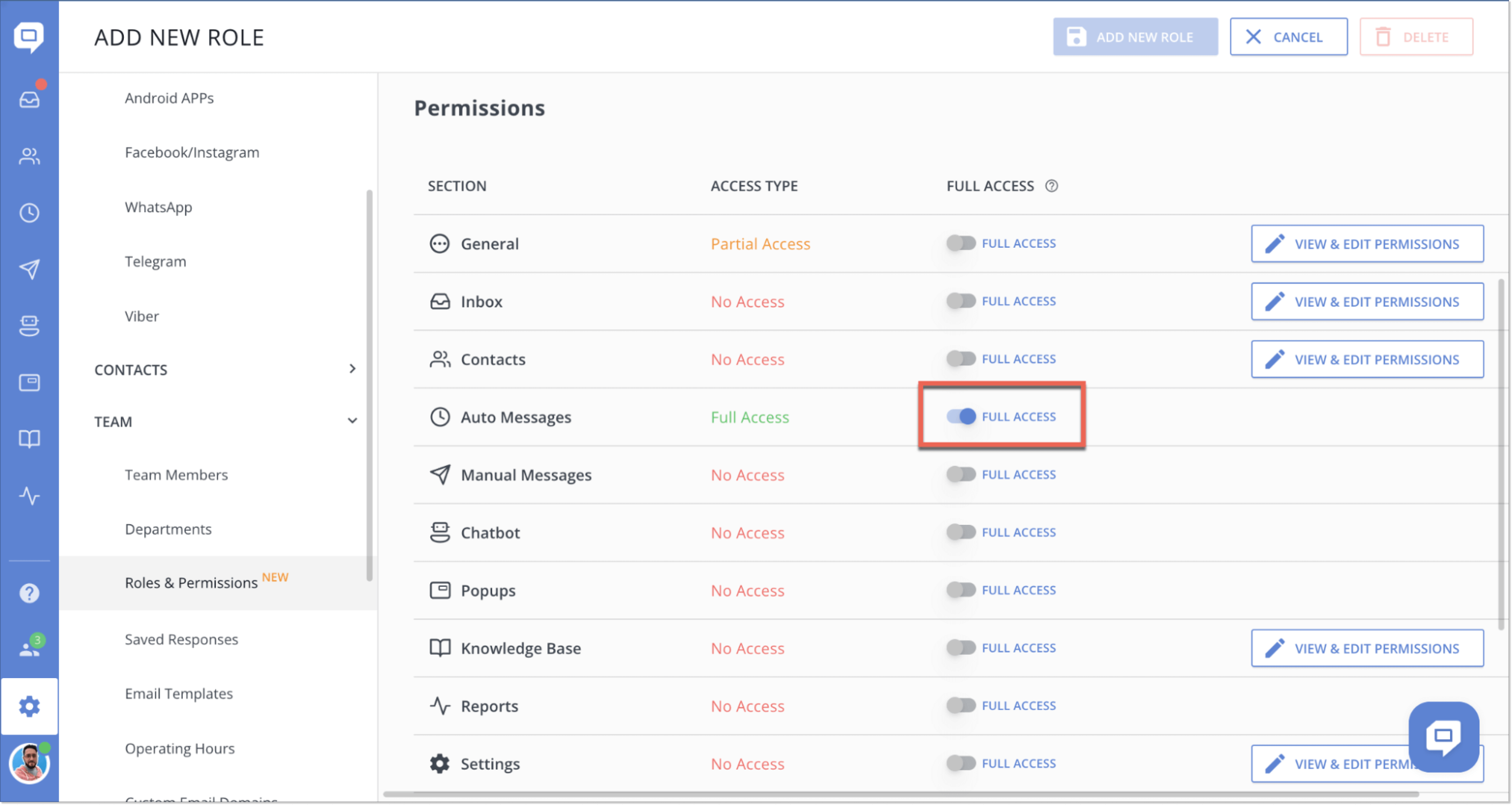
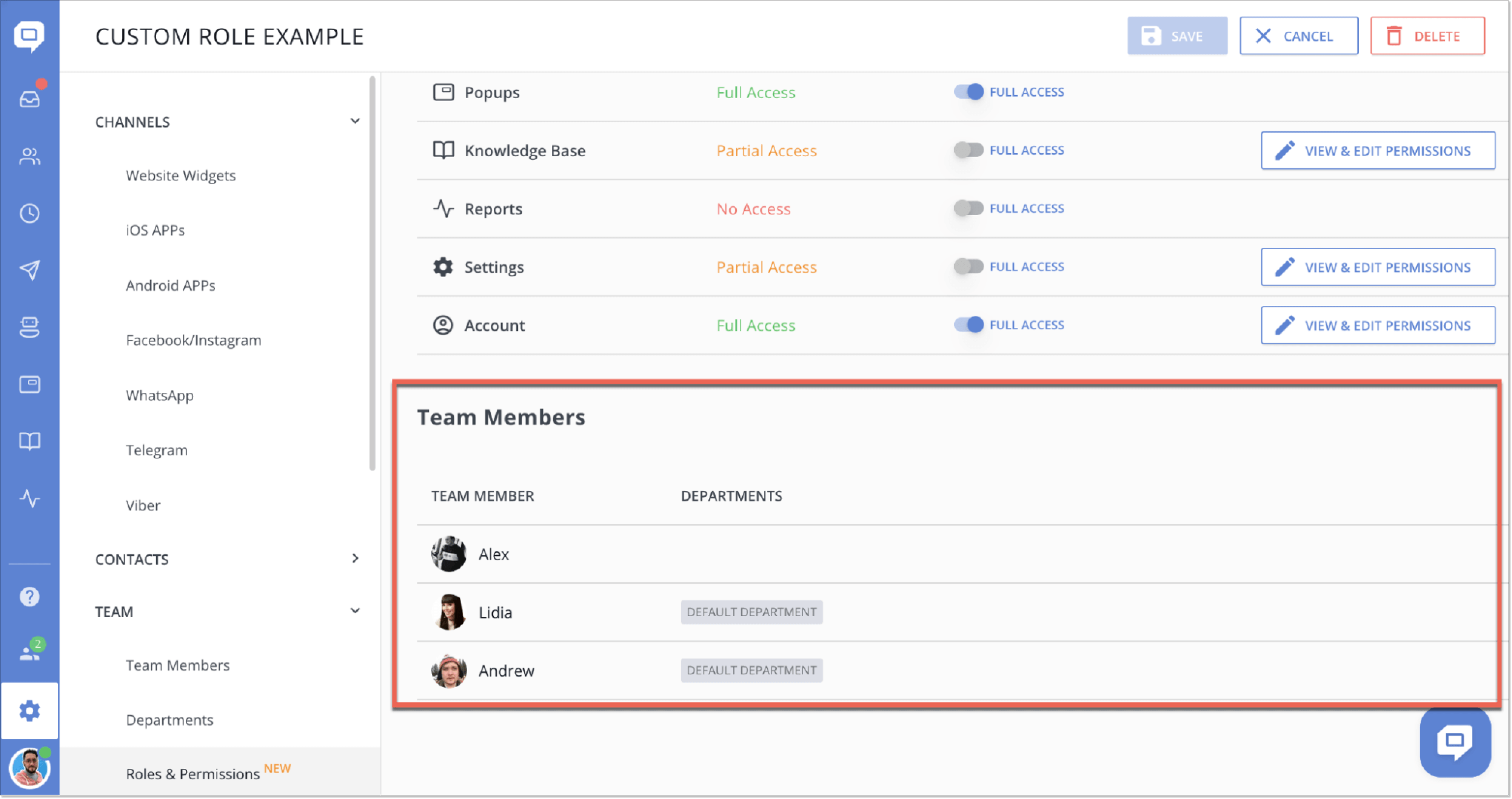
Also, you can now easily view all team members assigned to a specific role for added convenience.
The RBAC feature is only available in Pro and Unlim subscription plans:
With RBAC, managing roles and permissions has never been smoother. For more information, read our Knowledge Base article on the topic.
Read Also
🍁 Launch popups via JavaScript API, clickable phone number and more
Launch popups via JavaScript API, use hotkeys to mark chats read/unread, click to call users from their profiles, and smarter Assignment Rules.
🤖 Introducing HelpCrunch AI Agents: Multichannel and fully under your control
Meet HelpCrunch AI Agents! Handle up to 80% of customer requests automatically and scale your support while reducing costs.
📩 Custom domain for resending unseen chats: More control and branding
Resending emails with unseen chats now supports custom domains and unified settings. Check out more details!

