Chatbot vs. Virtual Assistant: What’s the Difference?
Confused by chatbots and virtual assistants? This guide clears it up with real examples and practical advice.
Written by Kateryna Havrylenko
Chatbots and virtual assistants are the same. We could end the conversation here, but I’m not here to mislead you. Sure, they look like they do the same job, and it might feel like someone just slapped a fancier name on the same idea. The truth is, there is a meaningful difference. Let’s break down chatbot vs. virtual assistant and understand what each one is actually meant to do.
What is a chatbot?
Let’s start with the basics: what is a chatbot, and how does it work? 🤔
A chatbot is a program that chats with users via text or voice. The main idea is simple: automate communication where a human isn’t really needed. Answering the same questions over and over, taking orders, or giving basic info – a chatbot can do all that without an operator.
There are two main types of chatbots, and the choice between them pretty much defines what you’ll get.
Rule-based chatbots follow a fixed scenario. The user picks an option from the menu or types a keyword, and the bot replies with a predefined answer. The logic is easy: If you choose A, you receive B. These bots are fast to set up, don’t need complex systems behind them, and work best for repetitive tasks.
AI-powered chatbots use artificial intelligence to understand context. They analyze messages using natural language processing, identify user intent, and can generate responses that don’t exist in a predefined database. This is conversational AI – a technology that makes dialogue more flexible and natural.
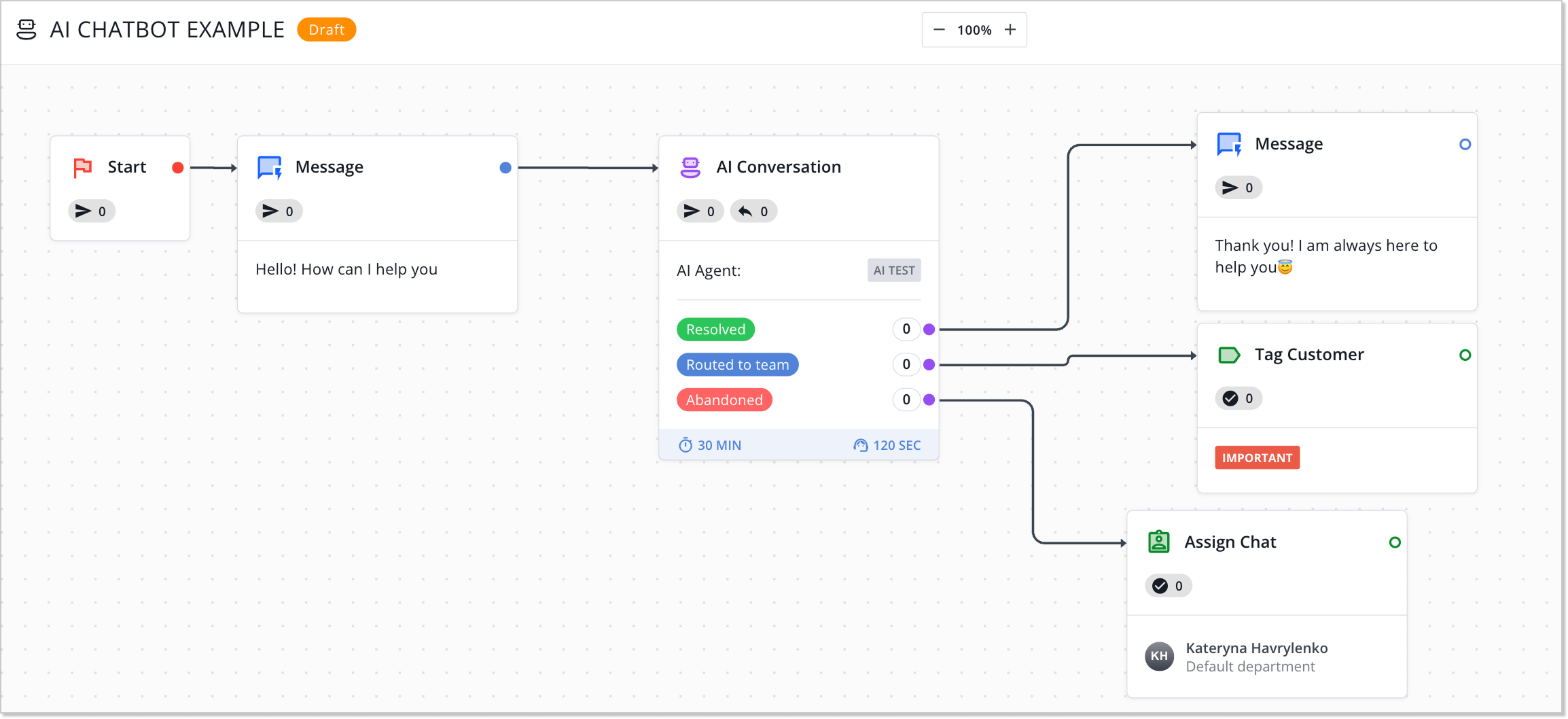
How chatbots work
A chatbot’s mechanics depend on its type. Rule-based systems function like a decision tree. Each user response leads to the next step in a predefined flow. You click “Yes” the bot moves to step A. You choose “No” it moves to step B. The limitation is obvious: if a request isn’t covered by the script, the bot won’t be able to help.
AI chatbots work differently. When a user sends a message, the system:
- Identifies the intent (what the user wants) and key entities (what the message is about).
- Uses machine learning to select or generate a response.
- Learns from previous chatbot conversations, improving accuracy over time.
What is a virtual assistant?
A virtual assistant is a system that can do things for you – set reminders, book meetings, find documents, or control your smart home. A virtual assistant works proactively, suggesting solutions, integrating with other services, and adapting to your habits.
You’ve probably used virtual assistants already, even if you never called them that. Google Assistant on your phone, Siri in Apple’s ecosystem, and Alexa on smart devices are classic examples. But modern AI virtual assistants go far beyond voice commands. They’re now part of enterprise workflows, run CRM systems, and even handle some operational tasks in business environments.
How virtual assistants work
Virtual assistants are built on a combination of artificial intelligence technologies: natural language processing to understand commands, machine learning to learn from user behavior, and are connected to external systems through integration APIs.
Here’s the process in a nutshell:
- Natural language understanding means the system gets not just the words you say, but the context and your intent.
- Integration with services lets it actually take action: create a task in Asana, ping someone on Slack, or tweak the office temperature.
- It handles tasks automatically, no manual work needed.
- The AI assistant remembers your preferences, spots patterns in your behavior, and uses them to make increasingly accurate predictions.
What is the difference between a virtual assistant and a chatbot?
Once we’ve defined chatbots and AI assistants, the difference is pretty obvious. But to be totally clear (and to keep our inner perfectionist happy), let’s break them down across the main criteria.
| Criterion | Chatbot | Virtual assistant |
| Tech and intelligence | Rule-based or AI using NLP to understand what’s asked. | Advanced AI – ML, NLU, generative AI that can pull data from multiple sources. |
| Functionality | Just communication. | Handles tasks. |
| Context understanding | Only remembers the current chat/session. | Covers the full ecosystem. |
| Learning capabilities | Rule-based bots don’t learn; AI bots improve within the conversation. | Learns from user behavior and adapts over time. |
| Integration | Single platform. | Multi-platform. |
Next, let’s dive into each of these criteria in detail.
Technology and intelligence level
Chatbots: rule-based bots stick to a fixed script. AI chatbots use natural language processing to figure out what the user wants, but they mainly focus on the conversation itself. They analyze your text, identify intent, and generate a response based on that.
Virtual assistants: built on more advanced architectures, combining machine learning, natural language understanding, and generative AI. They don’t just process your request; they pull context from multiple sources at once. Your assistant can make decisions using data from your CRM, calendar, email, and internal systems.
Functionality
Chatbots: answer questions, handle FAQs, and chat in support scenarios. They’re made for conversation, not action. If the client needs info, the chatbot will provide it. But changing a system, creating a task, or executing an operation is beyond its capabilities.
Virtual assistants: actually do things. Scheduling meetings, managing workflows, connecting with enterprise systems, or analyzing data. They act like a personal assistant or productivity tool – providing information and making changes to your workflows.
Context understanding
Chatbots: AI chatbots understand context within a single session. They remember what you said a few messages back and can keep the conversation going logically. But once the session ends, or info is needed from another system, the context disappears.
Virtual assistants: analyze context across the entire ecosystem. They know about upcoming meetings, the email sent yesterday, and next week’s project deadlines. AI assistants understand what’s going on around you, not just what you type, and can suggest actions without extra explanations.
Learning capabilities and adaptability
Chatbots: rule-based bots don’t learn. AI chatbots improve within the conversation – recognizing intent better, generating smarter responses, and handling unusual phrases. But they only adapt within that chat.
Virtual assistants: constantly learn from your habits. If you create certain tasks on Friday, the assistant will suggest this automatically. Need specific metrics ready before a meeting? They will put them in advance. Personalization happens at the process level, not just in chat.
Integration
Chatbots: usually live in a single platform: website chat, messenger, or app. They may have basic integrations like sending a ticket to a CRM or pulling a knowledge base article, but these are isolated connections.
Virtual assistants: hook into PM software, payment systems, CRM, smart devices. They don’t just read the data but act in it: create events, update statuses, send messages. Integration is their core, not an additional option.
I want to point out right away that these differences between chatbots and virtual assistants don’t make one tool better than the other. They simply make each suited for different tasks. The question isn’t which one is more powerful, but which one solves your specific problem more effectively.
Best use cases for chatbots and virtual assistants
The difference between chatbots and virtual assistants becomes most obvious in practice. Let’s look at real-world cases of companies that have already optimized their processes using these tools.
Real use cases for chatbots
A chatbot is ideal where users expect an instant answer, rather than a conversation with an assistant.
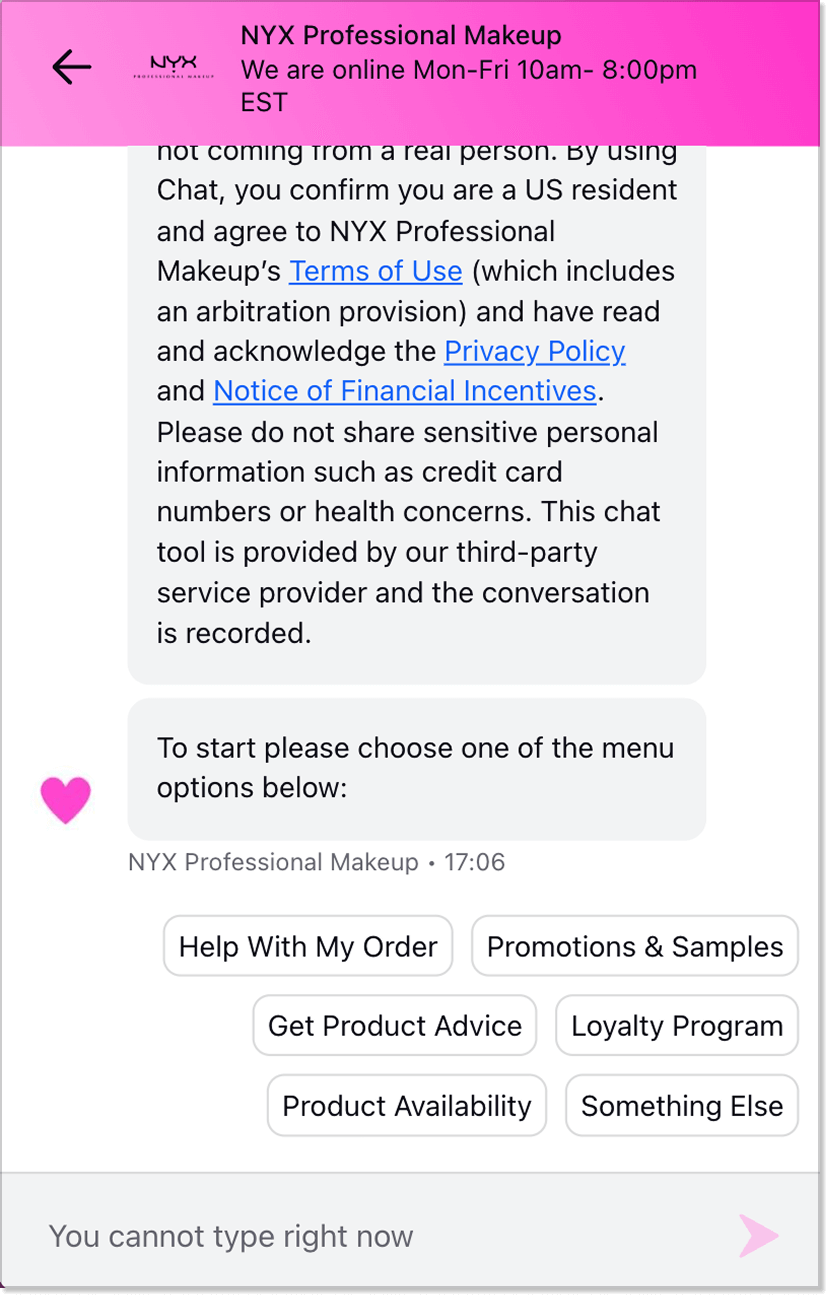
NYX
NYX, a cosmetics brand with a large online catalog, makes it easy for customers to get lost in the product selection. The company uses a chatbot to help users navigate products, provide order details, and answer basic support questions. For eCommerce stores, this is a prime example of how automated interaction can give customers the feeling of fast, “live” assistance even before contacting the support team.
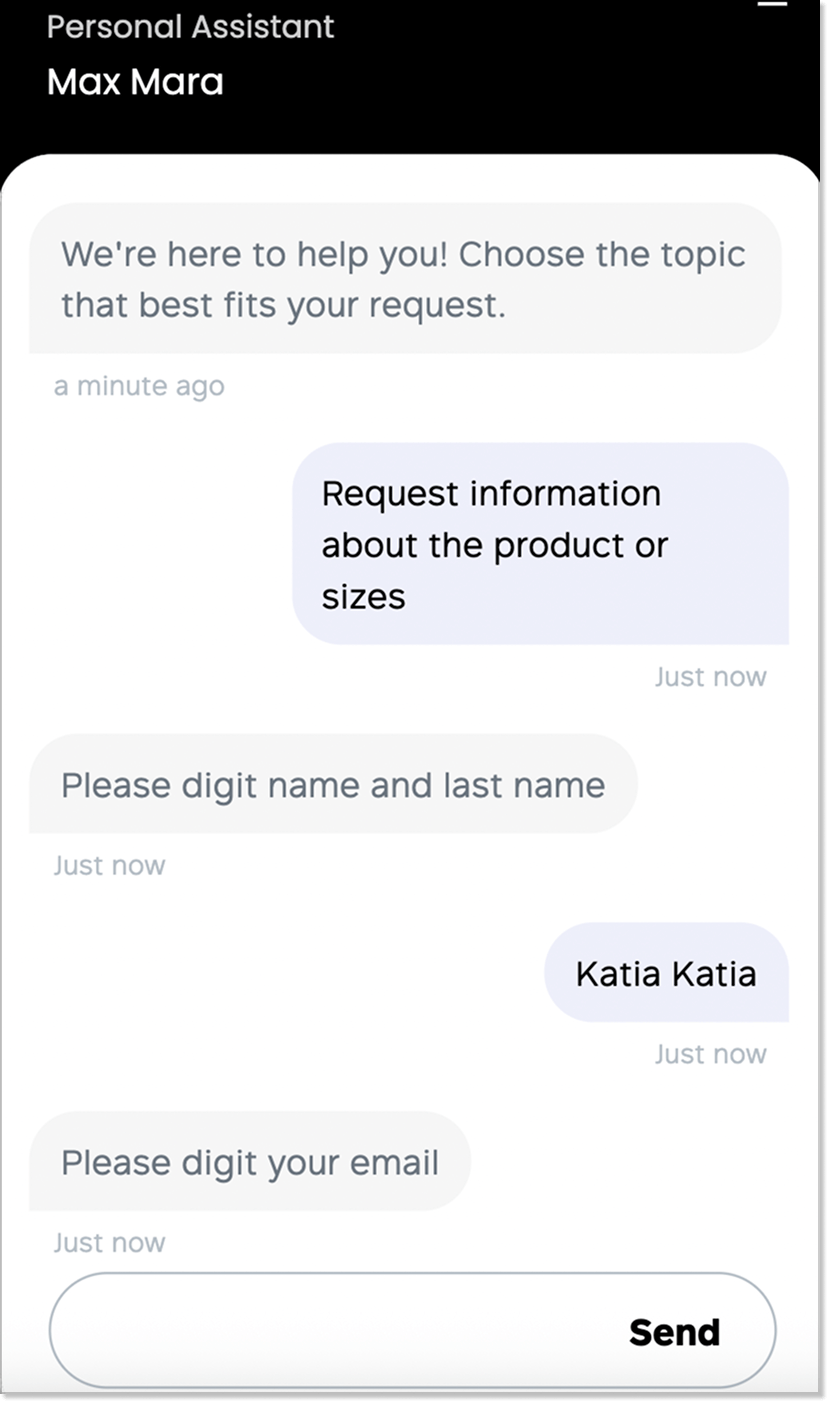
Max Mara
I used to think chatbots in fashion stores were mostly for show. Then I looked at Max Mara. Their chatbot actually helps: find the right product, check availability, and answer the usual “Do you have this in my size?” questions. Suddenly, buying feels less like a quest and more like… well, buying.
Real use cases for virtual assistants
A virtual assistant is all about context, logic, and complex actions. It helps users move toward a desired outcome.
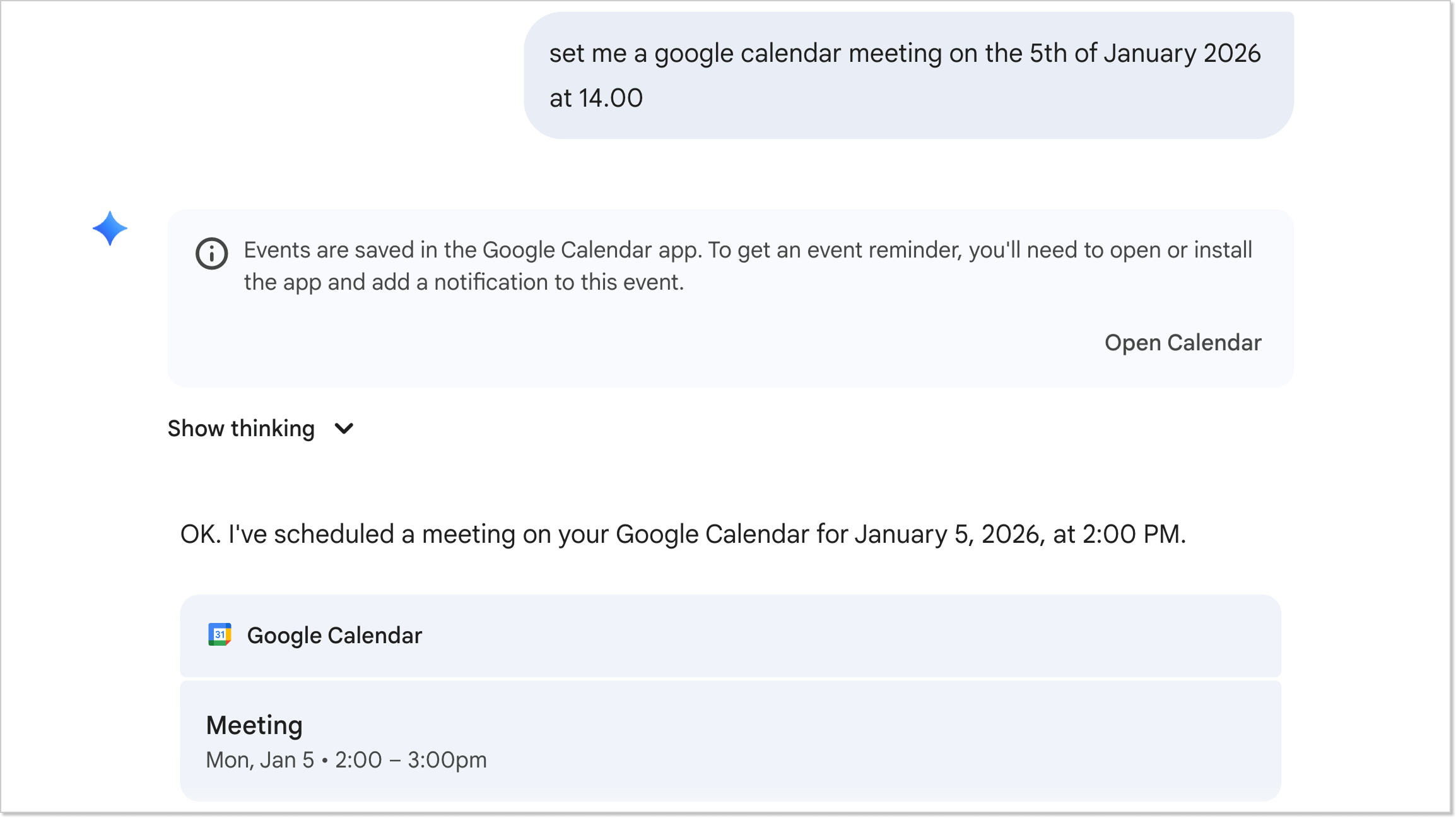
Gemini
Honestly, even I didn’t know Gemini could do this. Sure, it answers user questions and can even generate images from prompts – nothing too crazy. But here’s the kicker: now you can create Google Meet events and set reminders just by voice/text. Plus, you can use Gemini right inside Google Docs for writing, analyzing, or even design tasks.
GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot is basically a personal coding buddy. It looks at your existing code and suggests useful additions. Besides saving time, it helps you pick up best practices and solve typical coding problems faster. Life easier? Definitely.

Checklist: How to choose the right tool for your business?
If you’re already convinced that automating communication or operational workflows is what your business needs, the next logical question is: which tool should you choose? Here’s your cheat sheet and some recommendations for choosing the right one.
✅ Start with the problem, not the shiny tech
A common mistake is picking software just because “everyone’s using AI” or “it looks cool.” The smart move is to define the problem first. What’s not working? Are leads slipping away because nobody answers after working hours? According to Asana IT projects often fail because goals weren’t clear from the start.
✅ Know your team’s tech capabilities
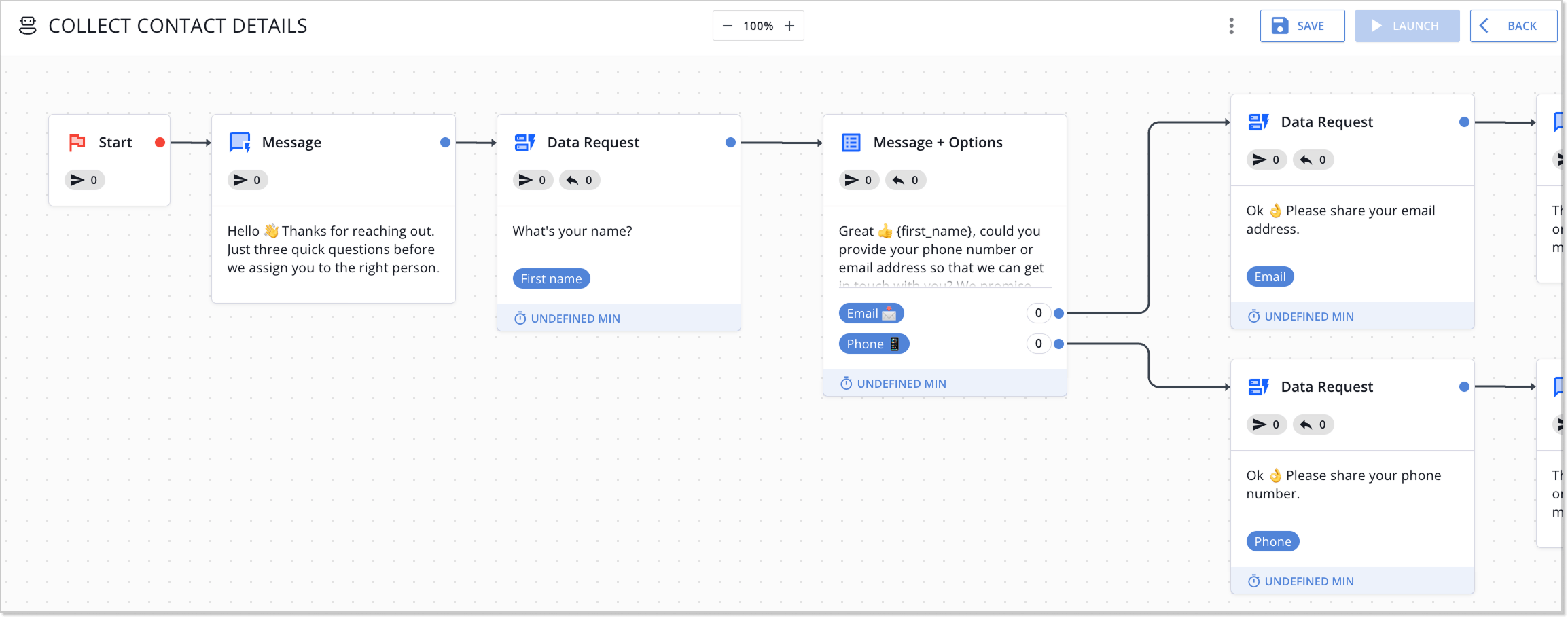
Some platforms require developers, others are no-code and can be launched by a marketer in an hour. If you don’t have an in-house IT team, stick with code-free solutions. HelpCrunch, for example, lets you build a chatbot with a visual editor: just create a flow, add conditions, and go – zero coding required.
✅ Check the true cost of ownership
Prices on website are just the tip of the iceberg. Real costs include setup, team training, support, extra integrations, and user or conversation fees. A “from $49/month” plan can balloon to $500 when you add messengers, analytics, and priority support.
Think about the total cost of ownership for a year. Sometimes a $200/month tool with smooth onboarding is cheaper than a “free” version that takes two weeks to set up.
✅ Test integrations before signing anything
No business works in a vacuum. Your chatbot or virtual assistant needs to plug into the tools you need. Check integrations on the platform’s site, but go further: try them out in a trial. If it doesn’t work with your core stack, it doesn’t matter how fancy the interface is.
✅ Check how the system learns (or doesn’t)
Ask your vendor: How often do models need updating? Does it learn from user feedback? Can it automatically improve based on past conversations? If these answers aren’t clear, get ready to manually fix errors down the line.
✅ Test with real scenarios, not demo data
Your customers don’t type perfectly. They make typos, use slang, ask multiple questions in one message, and expect the system to understand.
Run a trial and test the system on real customer support queries. See how it handles unusual phrasing, unknown terms, and multilingual dialogs. If you have an internal team, let them use the interface, they’ll quickly spot whether it’s convenient for daily use, not just one-time demos.
✅ Pay attention to support – you’ll need it
Even the simplest platform requires help at the start. Check what kind of support the vendor offers: live chat, email, or just documentation? How quickly do they respond?
Read reviews on G2, Capterra, and Trustpilot. Don’t just look at overall ratings, focus on mentions of support: do they respond quickly, give helpful answers, and have expertise in your industry? A platform with 4.8 stars but reviews saying “support doesn’t respond for weeks” is a red flag.
✅Don’t forget about security and compliance
If your chatbot handles customer data (and it likely does), ensure it’s GDPR, CCPA, or region-compliant. Where is the data stored? Who can access it? Can you control the permissions?
✅Give yourself room to fail
The smartest move is to start with a limited pilot project. Don’t roll the system out across the entire business right away. Pick one use case: automate FAQs on your site or delegate scheduling for one team. See how it performs in real conditions, where bottlenecks appear, and whether it really saves time. If after a month of testing it’s not working, it’s better to stop now than spend a year maintaining a system that doesn’t deliver.
Final word
Chatbot vs. virtual assistant isn’t about old vs. new or how advanced the technology is. It’s about different roles within a system. One is designed to respond quickly to requests and reduce the workload on your team. The other is built to take action and work with context.
That’s why the real question isn’t “Which one should I choose?” but “Where exactly is the problem?” If you need fast answers, that’s one scenario. If you need results and task execution, that’s a completely different one. The confusion ends here, and now you’re equipped with the knowledge. All that’s left is choosing the tool that actually works, not just one that sounds good.
FAQs
What is a chatbot and a virtual assistant?
A chatbot is a tool that responds to user messages and automates conversations. A virtual assistant is an AI system that understands context and performs tasks across tools and workflows.
Can a chatbot and a virtual assistant work together on the same website?
Absolutely, and this is often the best strategy. Many modern platforms use a hybrid model where a simple chatbot greets the user and handles basic filtering, then passes the conversation to a virtual assistant if the request becomes complex or requires accessing personal account data.
Is there a difference between chatbots and conversational AI?
Yes. In the conversational AI vs. chatbot comparison, chatbots handle predefined or simple conversations, while conversational AI understands context and generates more flexible, natural responses.
Is an AI agent a chatbot or a virtual assistant?
Neither. An AI agent is a more advanced evolution of both. While chatbots converse and virtual assistants assist, AI agents are goal-oriented software that can think, plan, and execute multistep tasks independently with minimal human input.